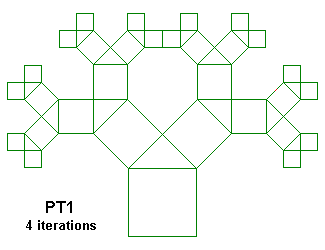
PT1 {; Pythagorean Tree
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Figure 2.63, p. 127
Angle 8
Axiom F++F[A]++F[B]++F
A=-@IQ2F[A]++F[B]++F++F
B=---@IQ2F++F[A]++F[B]++F
}
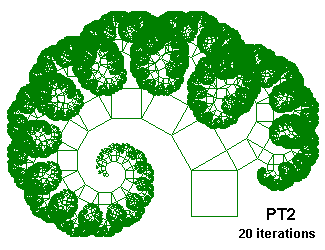
PT2 {; Pythagorean Tree
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Figures 2.64 and 2.65, p. 128 and 129
; .866 is sqrt(3)/2
; The two triangles are always attached in same orientation
Angle 12
Axiom F+++F[A]+++F[B]+++F
A=--@.5F[A]+++F[B]+++F+++F
B=-----@.866F+++F[A]+++F[B]+++F
}
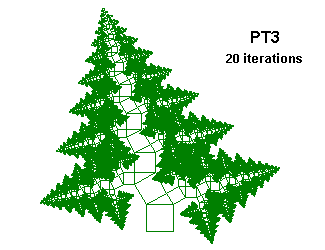
PT3 {; Pythagorean Tree
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Figures 2.64 and 2.65, p. 128 and 129
; .866 is sqrt(3)/2
; The two triangles flip their orientation after each step
Angle 12
Axiom F+++F[A]+++F[B]+++F
A=--@.5F[P]+++F[Q]+++F+++F
B=-----@.866F+++F[P]+++F[Q]+++F
P=-@.866F[A]+++F[B]+++F+++F
Q=----@.5F+++F[A]+++F[B]+++F
}
PT4 {; Broccoli-Like Phythagoras Tree
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Figure 2.67, p. 130
; Using D, \nn and /nn
; .532 is 1/(2cos20°)
Angle 3 ; Only to avoid errors, we do not use this angle
Axiom D\90D[A]\90D[B]\90D
A=/20@.532D[A]\90D[B]\90D\90D
B=/160@.532D\90D[A]\90D[B]\90D
}
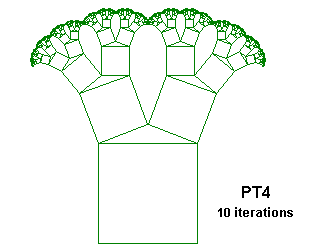
PT5 {; Pythagorean Tree
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Inspired on Figures 2.64 and 2.65, p. 128 and 129
; Construction with a triangle of sides 3, 4 and 5
; Using D, \nn and /nn, 53.13° is acos(3/5)
Angle 3 ; Only to avoid errors, we do not use this angle
Axiom D\90D[A]\90D[B]\90D
A=/53.13@.6D[A]\90D[B]\90D\90D
B=/143.13@.8D\90D[A]\90D[B]\90D
}
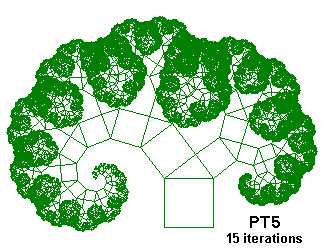
PT6 {; Pythagorean Tree
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Inspired on Figures 2.64 and 2.65, p. 128 and 129
; Construction with a triangle of sides 3, 4 and 5
; Using D, \nn and /nn, 53.13° is acos(3/5)
Angle 3 ; Only to avoid errors, we do not use this angle
Axiom D\90D[A]\90D[B]\90D
A=/53.13@.6D[P]\90D[Q]\90D\90D
B=/143.13@.8D\90D[P]\90D[Q]\90D
P=/36.87@.8D[A]\90D[B]\90D\90D
Q=/126.87@.6D\90D[A]\90D[B]\90D
}
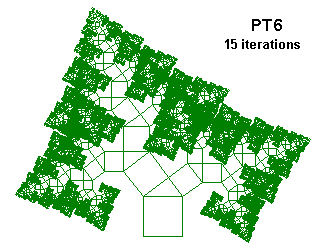
PT7 {; Pythagorean Tree
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Inspired on Figures 2.64 and 2.65, p. 128 and 129
; Construction with a triangle of sides 5, 12 and 13
; Using D, \nn and /nn, 67.38° is acos(5/13)
Angle 3 ; Only to avoid errors, we do not use this angle
Axiom D\90D[A]\90D[B]\90D
A=/67.38@.3846D[A]\90D[B]\90D\90D
B=/157.38@.9231D\90D[A]\90D[B]\90D
}
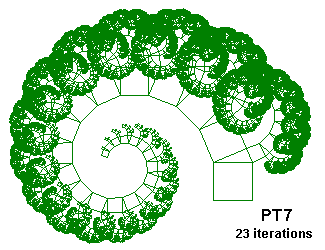
PT8 {; Pythagorean Tree
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Inspired on Figures 2.64 and 2.65, p. 128 and 129
; Construction with a triangle of angles 40°, 50° and 90°
; Using D, \nn and /nn, .643 is cos50°
Angle 3 ; Only to avoid errors, we do not use this angle
Axiom D\90D[A]\90D[B]\90D
A=/50@.643D[A]\90D[B]\90D\90D
B=/140@.766D\90D[A]\90D[B]\90D
}
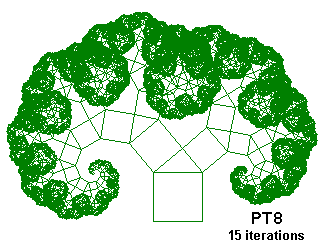
PT9 {; Phytagorean Tree constructed over a rectangle
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Inspired on Figures 2.64 and 2.65, p. 128 and 129
; .866 is sqrt(3)/2
Angle 12
Axiom F+++FF[A]+++F[B]+++FF
A=--@.5FF[A]+++F[B]+++FF+++F
B=-----@.866F+++FF[A]+++F[B]+++FF
}
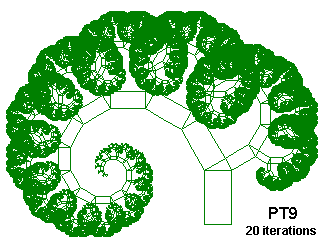
PT10 {; Broccoli-Like Phythagoras Tree over a rectangle
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Inspired on Figure 2.67, p. 130
; Using D, \nn and /nn
; .532 is 1/(2cos20°)
Angle 3 ; Only for to avoid errors, we not use this angle
Axiom DD\90D[A]\90DD[B]\90D
A=/20@.532D[A]\90DD[B]\90D\90DD
B=/160@.532DD\90D[A]\90DD[B]\90D
}
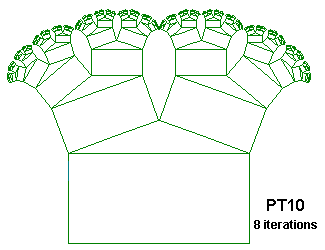
PT11 {; Phytagorean Tree
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Inspired on Figures 2.64 and 2.65, p. 128 and 129
; .866 is sqrt(3)/2
; The triangle on the right flips his orientation after each step
; The triangle on the left is always attached in the same orientation
Angle 12
Axiom F+++F[A]+++F[B]+++F
A=--@.5F[P]+++F[Q]+++F+++F
B=-----@.866F+++F[A]+++F[B]+++F
P=-@.866F[A]+++F[B]+++F+++F
Q=----@.5F+++F[A]+++F[B]+++F
}
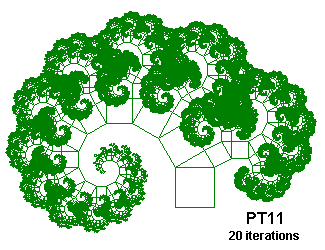
PT12 {; Phytagorean Tree
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Inspired on Figures 2.64 and 2.65, p. 128 and 129
; .866 is sqrt(3)/2
; The triangle on the left flips his orientation after each step
; The triangle on the right is always attached in the same orientation
Angle 12
Axiom F+++F[A]+++F[B]+++F
A=--@.5F[A]+++F[B]+++F+++F
B=-----@.866F+++F[P]+++F[Q]+++F
P=-@.866F[A]+++F[B]+++F+++F
Q=----@.5F+++F[A]+++F[B]+++F
}
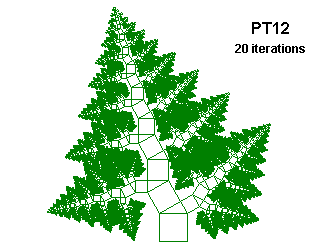
PT13 {; Phytagorean Tree, using G
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Inspired on Figures 2.64 and 2.65, p. 128 and 129
; .866 is sqrt(3)/2
Angle 12
Axiom F+++F[A]+++G[B]+++F
A=--@.5F[A]+++G[B]+++F+++G
B=-----@.866G+++F[A]+++G[B]+++F
}
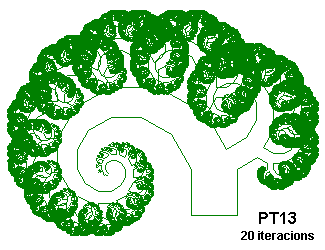
PT14 {; Phytagorean Tree, using G and over a rectangle
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Inspired on Figures 2.64 and 2.65, p. 128 and 129
; .866 is sqrt(3)/2
Angle 12
Axiom F+++FF[A]+++G[B]+++FF
A=--@.5FF[A]+++G[B]+++FF+++G
B=-----@.866G+++FF[A]+++G[B]+++FF
}
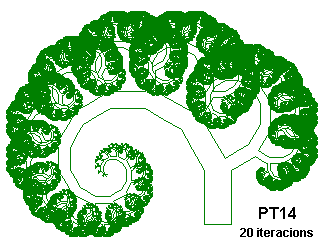
PT15 {; Phytagorean Tree, using G
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Inspired on Figures 2.64 and 2.65, p. 128 and 129
; .866 is sqrt(3)/2
Angle 12
Axiom F+++F[A]+++G[B]+++F
A=--@.5F[P]+++G[Q]+++F+++G
B=-----@.866G+++F[P]+++G[Q]+++F
P=-@.866F[A]+++G[B]+++F+++G
Q=----@.5G+++F[A]+++G[B]+++F
}
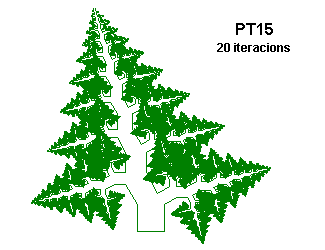
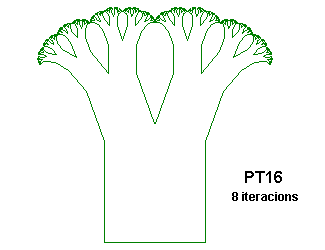
PT16 {; Broccoli-Like Phythagoras Tree, using D
; From "Chaos and Fractals" by Peitgen, Jürgens and Saupe
; Inspired on Figure 2.67, p. 130
; .532 is 1/2(cos20º)
Angle 3 ; Only for to avoid errors, we not use this angle
Axiom D\90D[A]\90M[B]\90D
A=/20@.532D[A]\90M[B]\90D\90M
B=/160@.532M\90D[A]\90M[B]\90D
}