|
A vector is an orientated segment. Two things characterize a vector:
1) Length of the segment. In mathematics this length is usually called modulus.
2) Direction given by the oriented straight that goes by him, or by any parallel oriented straight.
A vector does not have a defined location . A vector can go to any place of the plane without modifying neither his module, nor his direction. By this reason, it is said that vectors are free.
We express a vector with a minuscule letter, we express the origin and the end of a vector with two capital letters. For example, 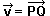 indicates the vector which has origin in the point P and end in the point Q. indicates the vector which has origin in the point P and end in the point Q.
Whenever it was possible, we will put an arrow above to indicate that an object is a vector: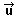 , ,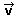 , ,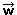 , ... , ...
Vectors are good for representing geometric and physical magnitudes that have modulus and direction, as translations, velocity and forces.
|