|
ACTIVITY 3.1 |
|||
| Remember that the module of a vector is the length of the orientated corresponding segment. The module of a vector is always a positive number and only the null vector has module zero. The module of the vector Knowing the vector components | This procedure to calculate the module may apply much if the components
are positive, like |
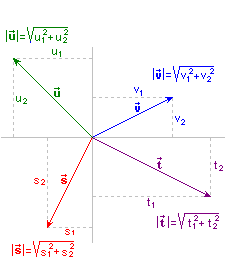 |
|
INTERACTIVE ACTIVITY This vector has module 4, that you can vary moving the green point, and direction that you can not vary. That is to say, you can not vary the angle 70,25 º that forms with the semi axis positive OX (this angle is the argument, and we will study it in next activity). 1) You build vectors with the same direction, but with the following modules: 2) Can you manage his module to be -2 or any negative quantity? 3) Can you manage his module because it will be zero? 4) Where the extreme of all the vectors that have same direction and way are situated if we draw them with the same origin? |
|
| HOMEWORK |
You draw in the same coordinated plane the following vectors and you calculate his module:
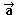 =
(3,4) =
(3,4) |
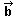 =
(-12,5) =
(-12,5) |
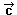 =
(-6,-6) =
(-6,-6) |
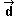 =
(8,-6) =
(8,-6) |
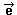 =
(0,5) =
(0,5) |
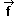 =
(-7,0) =
(-7,0) |
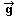 =
(0,-4) =
(0,-4) |
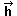 =
(1,0) =
(1,0) |
|
END OF ACTIVITY 3.1 |
|||