|
ACTIVITY 3.7 |
|||
|
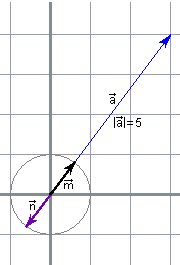
If they give us a vector
For instance, if If we would have interested in a vector of module 1 with opposite direction that Vectors of module 1 are called unit vectors or versors. |
|
|
INTERACTIVE ACTIVITY In the applet of the right side you have a vector You get untied vectors
|
|
| HOMEWORK |
| a) |
b) |
c) |
d) |
|
END OF ACTIVITY 3.7 |
|||