|
ACTIVITY 4.8 |
|||
|
In this activity we will study
what it happens with
vectors Put
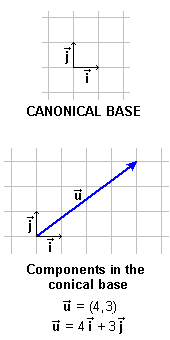
a vector Vectors Surely you will ask yourself about how are the "habitual" components of a vector, now we will call them components of the canonical base. Be patient: the importance of all that we have explained you, you will see it in the next activity, where you will see that it can be bases not canonical and components of a vector in a non canonical base. |
|
|
INTERACTIVE ACTIVITY a) Draw the
next given vectors such as linear combinations of vectors
b) Draw the
next given vectors by its components in the base
|
|
| HOMEWORK |
|
1) Which are the components of vectors
2) How would you express a given vector in a polar form Ma like linear combination of vectors
|
|
END OF ACTIVITY 4.8 |
|||