Ramon González
Calvet
Ph. D. (1993)
Mathematics
teacher
Head of department
Institut Pere Calders
08193 Cerdanyola del Vallčs
Spain
Phone +34-935801477
Fax: +34-935808621
rgonzalezcalvet gmail.com gmail.com
Not belonging to any social network
|
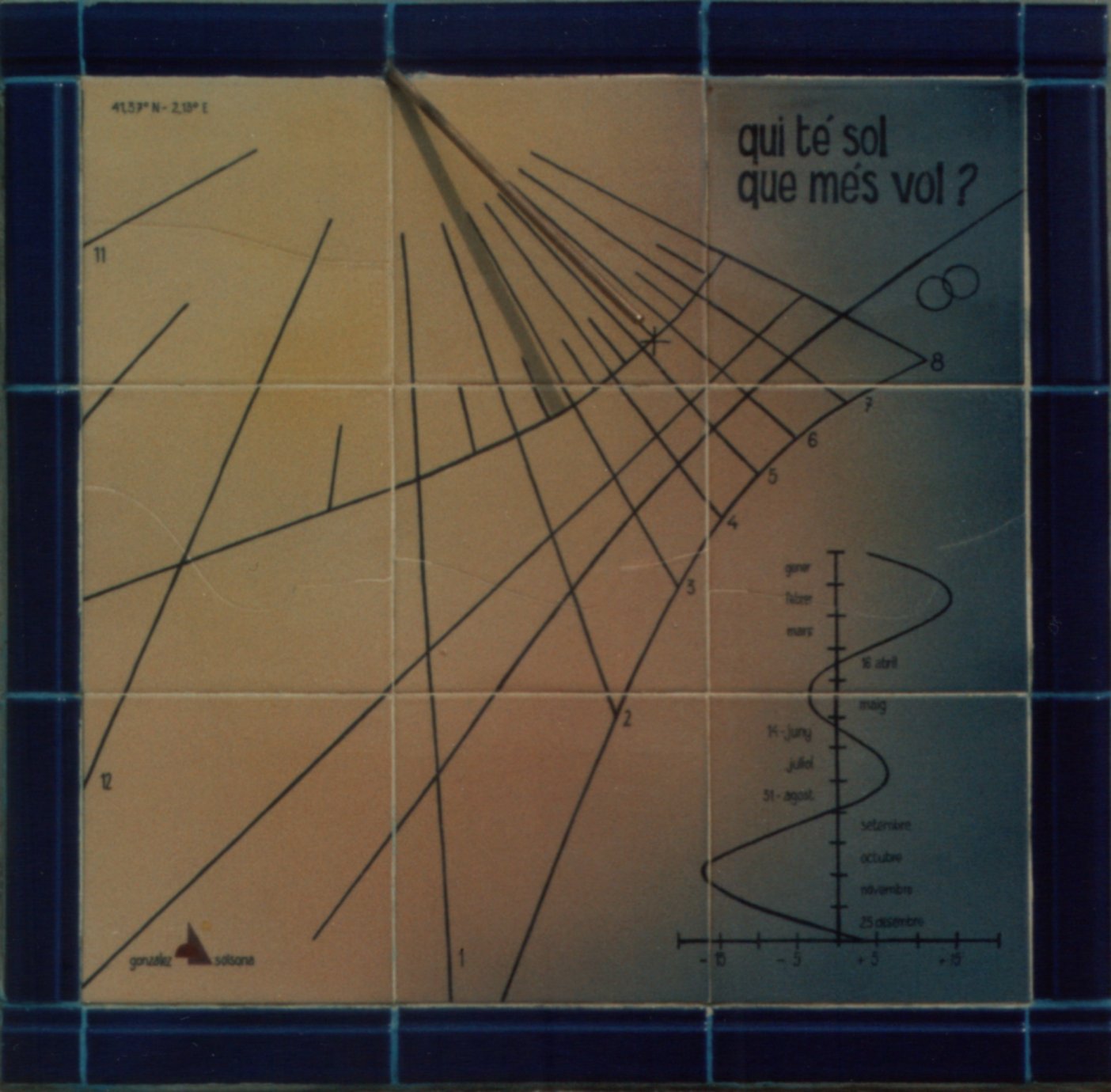
Sundial at 41.37°N 2.13°E (Barcelona) calculated and built by Ramon
González and Jordi Solsona. The rings remind the homeowners of their
wedding anniversary. The sundial reads Who has sun what else does
he want?
© Ramon González & Jordi Solsona
|
On Astronomy
On this webpage, there is a list of my publications about
astronomy, as a result of the discovery of the solution to the
three-body problem and to the N-body problem. Although I proved them many
years ago, it is only recently that I have developed their practical application to
astronomical systems.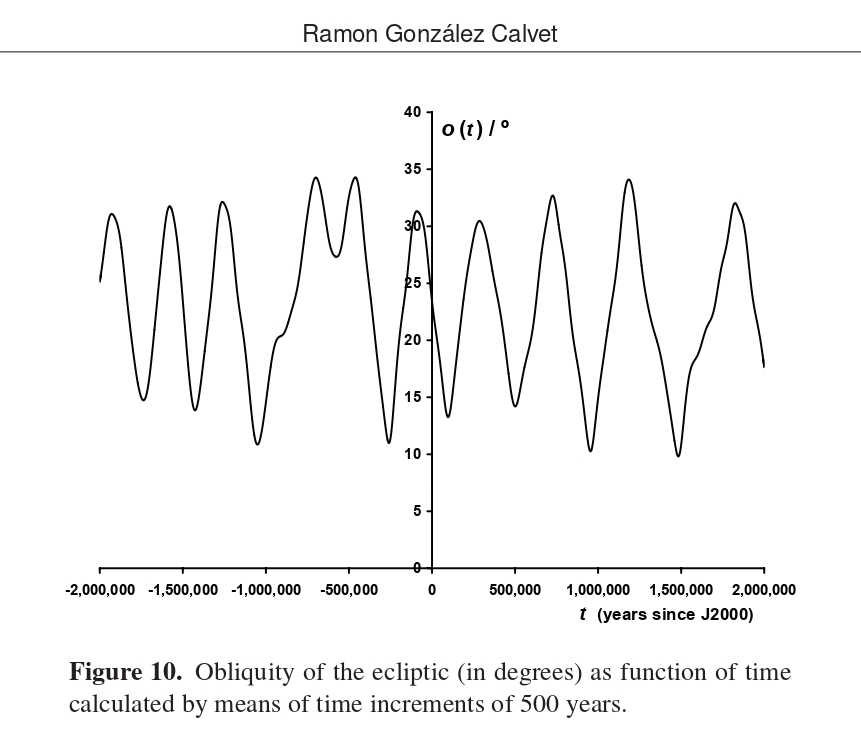
The first papers are in Djvu format. You can download
a Djvu viewer from Djvu.org.
R. Gonzalez, "The
Solution to the Three-Body Problem and Some Applications",. J. of
Geometry and Symmetry in Physics 49 (2018) 1-61.
R. González, "On
a New Analytic Theory of the Moon's Motion I: Orbital Angular Momentum", J.
of Geometry and Symmetry in Physics 57
(2020) 1-43.
R. González, "On
a New Analytic Theory of the Moon's Motion II: Orbit and Length of Months",
J. of Geometry and Symmetry in Physics 58
(2020) 13-54.
R. González, "On
a New Analytic Theory of the Moon's Motion III: Further Corrections",
J. of Geometry and Symmetry in Physics 59
(2021) 67-99.
R. Gonzalez, "On
the Dynamics of the Solar System I: Orbital Inclination and Nodal Precession", Geometry,
Integrability and Quantization 23 (2022) 1-38.
R. González, "On
the Dynamics of the Solar System II: Evolution of the Orbital Planes of the
Planets, Geometry, Integrability and Quantization 24 (2022) 39-64.
R. González, "On
the Dynamics of the Solar System III: Perihelion Precession and Eccentricity
Variation, Geometry, Integrability and Quantization 25 (2023) 1-45.
The reader can find a short summary of the theory of the
Moon's motion in the article "Lunar
theory" on the Wikipedia. Unfortunately, this content has been censured
by a Wikipedia editor. However, you can still acces it by going to "View
history" and accessing the version stored on July 31th, 2021.
The summary is entitled "Analytic theory of the main lunar problem with
relative coordinates".
In the paper on the evolution of the orbital planes of the
planets, as a colofon, the evolution of the obliquity
of the ecliptic was calculated since -2.000.000 BC till 2.000.000 AD as shown in
this figure.
Last update: June 24th,
2023

