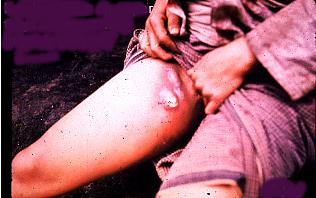
BUBONIC PLAGUE SYMPTOMS
Those are the symptoms of bubonic plague:- Blister at fleabite site
(Blisters: They can form if shoes always rub the same spot. Wearing shoes that do not fit or wearing shoes without socks can cause blisters. Blisters can become infected).
- High fever
(Fever: Raised body temperature usually with other symptoms.
A fever usually means the body has raised its temperature to fight an infection or condition).- Chills
(Chills: Excessive feeling of coldness. A person with severe chills feels excessively cold and may be shivering, even when wrapped in blankets)
- Headache
(Headache: Pain affecting the head or brain area)
- Swollen glands
(Swelling symptoms: Symptoms causing swelling or enlargement. Parts of the body may swell in response to injury, infection or disease)
- Swollen groin, armpit or neck lymph nodes
(Lymph nodes: Small, bean-shaped organs of the immune system distributed throughout the body tissue. Lymph nodes often swell in response to infection or disease. The lymph nodes are small nodules that form part of the lymphatic system, which distributes various immune-related cells around the body. Lymph nodes tend to swell if there is a nearby infection, because the lymph nodes are involved in the immune system's fight against the infection)
- Lymph node ulcers
(Ulcer: A break in the skin extending to all its layers that fails to heal and is often accompanied by inflammation)
- Extreme exhaustion
(Exhaustion: The inability to give a normal response until a certain recovery period. Disease may predispose to mental or physical tiredness)
- Prostration
(Prostration: Extreme exhaustion and fatigue)
- Delirium
(Delirium: Severe state of mental confusion)