|
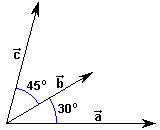
ACTIVITY 5.4 |
|||
|
The scalar product of two vectors is distributive with respect to the sum of vectors:
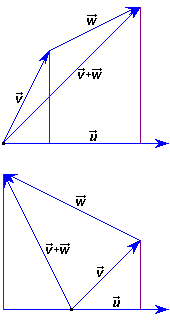
To demonstrate it, we take into account (superior figure in the right side): 1) Firstly, we can calculate 2) However,
you can see in the figure, the projection of a sum of vectors on
another vector, is the same that the sum of projections: 3) Linking the two previous identities , we have:
It can object
that we have prepared the upper figure on the right side very well to make the
affirmation
2). What does it happen if the projection on |
|
|
INTERACTIVE ACTIVITY The figure of the right side manifests the
distributivity Check that also is verified this distributivity when: 1) The projection
of 2) The
projection of 3) Two previous
directions (of
|
|
| HOMEWORK |
|
Give you three vectors
|
|
|
END OF ACTIVITY 5.4 |
|||